Breaking News
WHO holds emergency meeting as multiple nations implement Africa travel restrictions over new COVID variant concerns
The WHO is expected to name the heavily mutated variant Nu as health officials call it a “matter of concern.”

[KIRKLAND, Wash.] – (MTN) World health officials are alarmed due to a new fast-spreading Covid-19 variant in South Africa causing the World Health Organization to hold an emergency meeting as Asian stock markets plunged and the Dow Jones futures dropped 735 points.
The new variant, so far identified as B.1.1.529 has not been named, but the WHO is expected to assign it a name today, likely the Nu variant.
The variant was first detected in Botswana but has quickly spread in South Africa and two travel-related cases have been confirmed in Hong Kong. Botswana officials stated the four detected cases are among fully vaccinated individuals. in South Africa, cases are increasing rapidly in Gauteng Province, home to Johannesburg and one of the largest air travel hubs on the continent. In the span of a week, new cases went from a cluster to growing so fast scientists believe it has achieved community spread.
Officials in the U.K. are taking no chances. Health Secretary Sajid Javid announced that six African nations – South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Lesotho, and Eswatini – have been placed on the red list, placing strict rules on air travel.
Starting on Friday, any non-UK and Irish residents will be banned from entering England if they have been in the red list countries in the last ten days. Beginning Sunday, British nationals who have been in those countries will be required to quarantine upon entry. Additionally, health officials in the UK are asking anyone who has traveled to the impacted regions to get a PCR test as soon as possible.
South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor said the travel restrictions “seems to have been rushed,” in a statement where he expressed concern over the impact on tourism and business.
Israel and Singapore joined the U.K. early on Friday and added Mozambique to their travel restriction lists.
New case rate growth is much faster than Delta, which indicates the potential for a very high R0, or “r-naught,” which is the measure of how transmissible a communicable disease is. In little more than two weeks, B.1.1.529 has grown to almost 90% of all detected cases in South Africa.
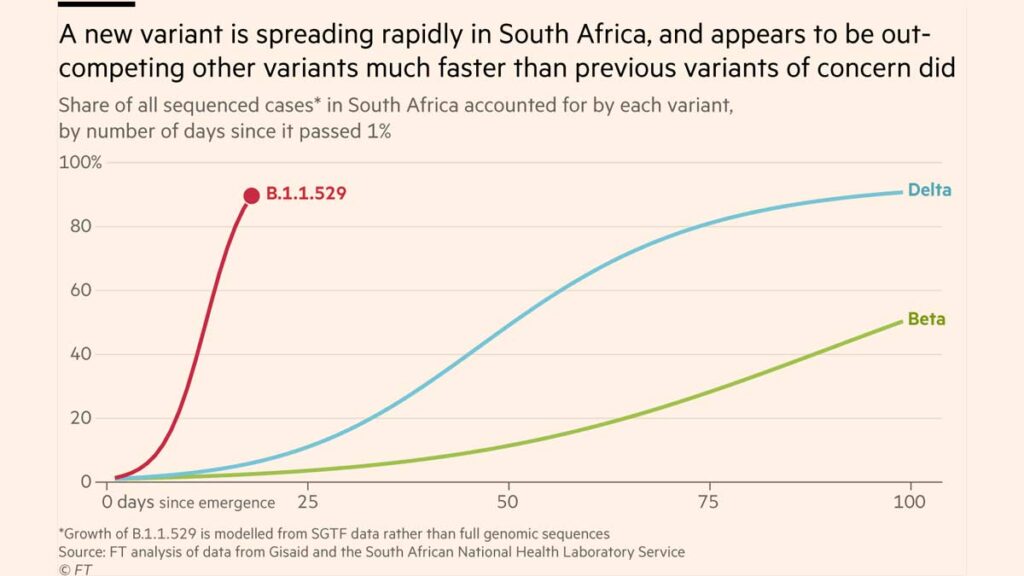
According to Johns Hopkins University, only 24.11% of South Africans are fully vaccinated which would aid a new variant to spread unchecked. Health officials in South Africa and with the WHO are concerned that the new variant is circulating more widely than current data suggests.
The B.1.1.529 has more than 50 mutations, which is significantly higher than any other viable variant previously seen. More than 30 of those alternations are changes to the spike protein, which is the mechanism that enables the SARS-CoV-2 virus to identify hosts cell and is the primary target of the body’s immune response.
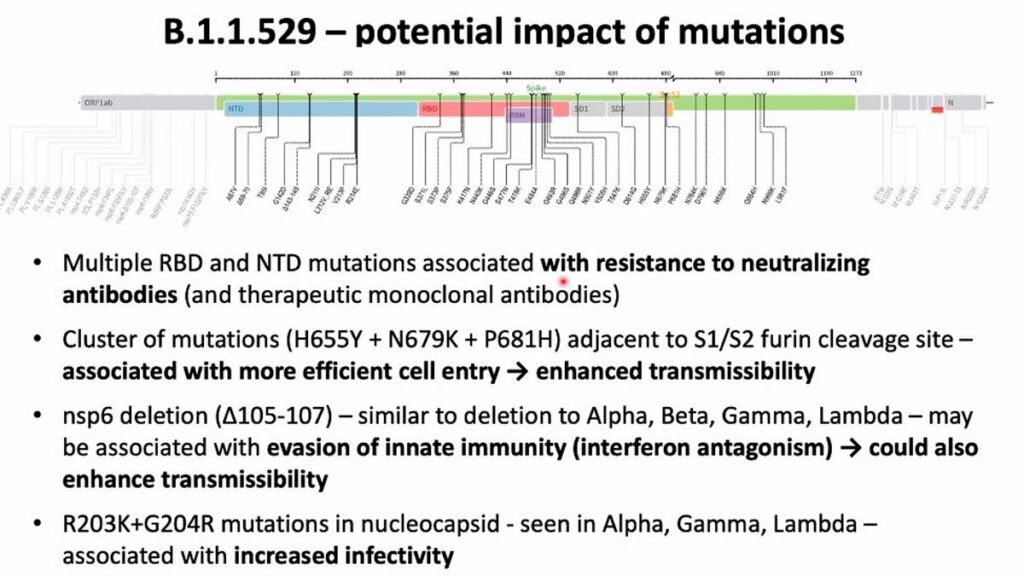
In a report published by the Journal Nature, Penny Moore, a virologist at the University of Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, indicated that computer models suggest not only does B.1.1.529 have mutations that are already known to aid in evading an immune response from B cells but could fool the body’s T cells.
B cells do the yeoman’s work of fighting virus infections, but have a shorter memory and can be tricked by a smaller set of mutations. T cells are the second line of immune defense with better memory and capabilities to spot mutations. When T cells identify a threat that was initially missed, they summon B cells to aid in the response. This is how disease acquired and vaccine immune response works. If the new variant is capable of evading T cells then the benefits of vaccine immunity would be reduced and disease acquired immunity could be rendered ineffective.
Disease acquired and vaccine immunity works the same. Antibodies bind to the spike proteins preventing the virus from entering cells so it can replicate. If the antibodies can’t bind to spike mutations and the mutations still enable the SARS-CoV-2 virus to identify host cells, the virus can spread inside the body unchecked causing a Covid-19 infection.
Another challenge is if these findings are accurate – the new variant may be capable of outmaneuvering monoclonal antibodies – blunting a critical early treatment.
One mutation is helping scientists track the spread of the new variant. A specific mutation to the spike protein enables researchers to identify the variant through a standard PCR test instead of waiting for genomic sequencing.
Currently, there are more questions than answers. Researchers know the new variant is spreading rapidly in South Africa and causing a new surge. What is not known is if the rapid spread is being driven by a mostly unvaccinated population or because it is more transmissible. It also is not known if the new variant causes equal, more severe, or mild illness. There is no data about the capability the new antivirals Molnupiravir and Paxlovid could have in fighting B.1.1.529.
It is important to note that Beta, Gamma, and Mu were previous variants found to have high resistance to vaccine and disease acquired immunity but weren’t very transmissible. All three variants faded out because Delta was more contagious. In the simplest terms, Delta outbred the other variants. A key requirement for a new variant to spread rapidly would be the capability to outrun Delta.
Most important of all, there is no concrete scientific evidence that B1.1.529 is evading viral vector or mRNA-based vaccines. Previous variants have taken months to identify while this one was found, sequenced, and placed under investigation in a matter of days.
No cases have been detected in North America or any United States territories.