Health and Lifestyle
Scientists rush to understand the Omicron COVID variant as world leaders play politics
Epidemiologists call travel bans politically motivated and ineffective as more cases are detected in Europe.

[KIRKLAND, Wash.] – (MTN) Public health officials are scrambling to understand the seriousness of the Omicron Covid-19 variant as a growing list of nations report probable and confirmed cases.
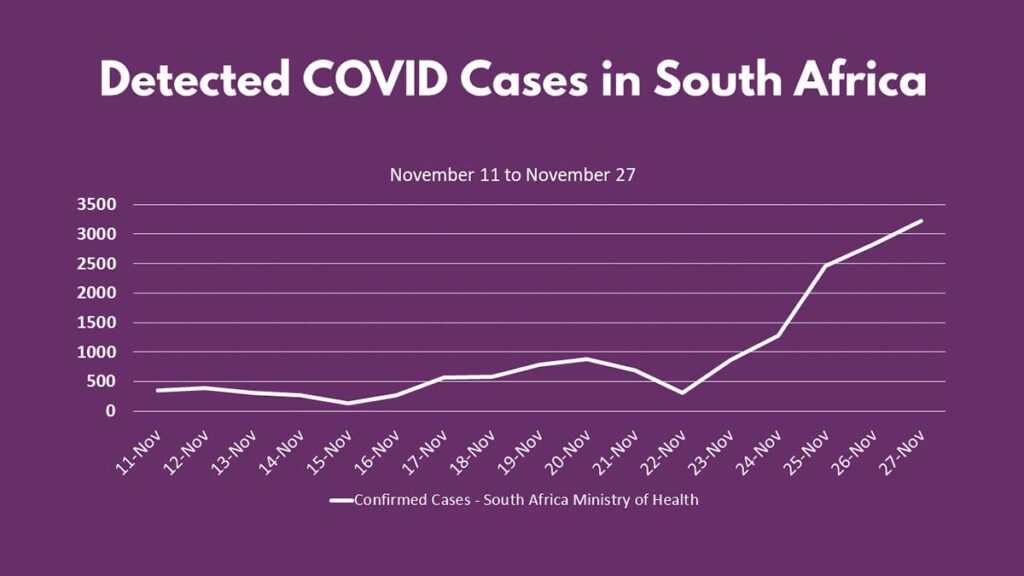
First confirmed on November 11 among four people from Botswana who had returned from traveling to neighboring South Africa, new cases in the nation of 59 million have leaped from 356 on the 11th to 3,220 on Saturday. Test positivity also increased dramatically in the last 16 days climbing from 1.1% to 9.2%. Test positivity over 5% is an indicator of under testing and over 7% is a signal there is growing community transmission.
On Friday, the World Health Organization (WHO) named the variant formerly known at B.1.1.529, Omicron, and labeled it a Variant of Concern (VOC). The variant has more than 50 mutations from the original COVID strain and shares many mutations with other VOCs. There are 32 mutations on the spike proteins, which can potentially impact transmissibility and increase the level of vaccine escape the Delta variant has.
Before the WHO met on Friday, new cases were confirmed in Israel, Belgium, and Hong Kong. By Saturday, Italy, England, Germany, and the Czech Republic have reported confirmed cases. Netherlands officials stopped two flights arriving from Johannesburg and retested more than 650 people for Covid-19, finding 61 new cases. The people who tested positive have been placed in isolation and their cases are being genetically sequenced to determine which variant they have.
On Friday evening all but two confirmed cases of the Omicron variant outside of the African continent were travel-related. One case in Belgium appears to have been caused by community spread. In Hong Kong, a person in a quarantine hotel became infected by another COVID positive occupant “across the hall.” The case detected in Belgium involves an unvaccinated individual while the Hong Kong case involves a person vaccinated in May or June.
Disinformation is spreading that cases are only among the vaccinated. South Africa had some early success in rolling out the COVID vaccine, but today only 24.11% of the population is fully vaccinated. Further misinformation that vaccines created the mutation isn’t supported or factual. Vaccines prevent mutations by reducing the number of people who can be infected and only 6% of all Africans are vaccinated against COVID. Because most recreational international travel requires a person to be fully vaccinated, travel-related cases are creating a short-term data fallacy.
Many nations including the United States and Canada have announced travel restrictions or bans to a varying list of six to ten countries in the southern part of Africa. Starting Sunday, air travel from South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Namibia, Lesotho, Eswatini, Mozambique, and Malawi will be restricted to US citizens and lawfully permanent residents. Delta and United Airlines have direct flights to South Africa from the United States.
A chorus of epidemiologists and health officials are calling the restrictions ineffective and politically motivated.
Based on the history of other variants it is likely Omicron was circulating before its November 9 detection. The United States relaxed air travel restrictions on November 8. There are no confirmed or suspected cases in North America, but infectious disease expert Dr. Anthony Fauci told reporters it is “possibly” already here.
One mutation is working in favor of public health and helping track the spread of the new variant. Omicron is missing a protein, and the absence can be detected by a PCR test. Genomic sequencing is still required for final confirmation, but the mutation makes probable cases easy to detect.
Pfizer and its Germany partner BioNTech as well as Moderna announced on Friday there were studying the efficacy of the currently available COVID vaccines and have plans to create an update if required. Both indicated research would take approximately two weeks and Pfizer stated a new vaccine could be available in 100 days, pending regulatory approval.
“From the beginning, we have said that as we seek to defeat the pandemic, it is imperative that we are proactive as the virus evolves,” said Moderna’s Chief Executive Officer Stéphane Bancel. “We have three lines of defense that we are advancing in parallel: we have already evaluated a higher dose booster of mRNA-1273, second, we are already studying two multi-valent booster candidates in the clinic that were designed to anticipate mutations such as those that have emerged in the Omicron variant and data is expected in the coming weeks, and third, we are rapidly advancing an Omicron-specific booster candidate.”
Doctors at UW Medicine in Seattle are studying the effectiveness of antiviral medications against the new strain. Dr. Deborah Fuller, speaking with local TV station KCPQ, did not specifically state if monoclonal antibodies such as Regeneron, molnupiravir by Merck, or Paxlovid by Pfizer were being studied.
Regeneron has been an effective early treatment for COVID and is credited with preventing as many as 10,000 hospitalizations in Florida. Some of the mutations indicate that Omicron may be able to resist or escape the drug. Molnupiravir is an antiviral developed in 2019 as a treatment for Influenza, Ebola, and other viral infections. Research showed the oral medication halved severe Covid-19 infections and deaths and is pending Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Paxlovid was developed as a therapeutic for Covid-19 and was 89% effective at preventing hospitalization. The antiviral is also an oral medication and is being reviewed by the FDA to receive a EUA.
New York Governor Kathy Hochul declared a state of emergency on Friday evening ahead of any new case spikes. The declaration goes into effect on December 3 and will enable the state to increase hospital capacity and release funds to hire additional staff and medical supplies. When the United States State Department eased travel restrictions on November 8, New York City was the number one chosen destination for European travelers. Orlando and Phoenix were number two and three.
A lot more will be known in the next two to four weeks about Omicron. The three questions epidemiologists will be working to answer include does Omicron spread faster than Delta, can Omicron escape some of our therapies and public health measures, and if those sickened by the new variant suffer from equal, more severe, or more mild symptoms.
Public health officials recommend that getting vaccinated and getting your booster if you’re eligible, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and deferring travel are the best lines of defense until more is known. People who feel sick should not dismiss their symptoms as a cold or flu and should test for COVID. A positive result with a home test should be followed up with a PCR test to confirm the results and help public health track which variants are spreading.
The Washington State Department of Health is closed from Thursday to Sunday for the Thanksgiving holiday and has not made any statement.
As of Saturday afternoon, the number of confirmed cases globally can be counted in the dozens – caution and not panic should be the word of the day.












