International News
Part 3: The complex history of Islamic extremism and Russia’s contribution to the rise of Al Qaeda and ISIS
Part three of a ten part series explaining how a series of events starting in 1951 led to the creation of Al Qaeda and ISIS, and their mid-21st century resurgence.

This is part three of a ten-part series that explains the rise of modern Islamic extremism. From 1951 to 2021, a series of key geopolitical events, many independent of each other, caused the Islamic Revolution, the rise of Al Qaeda and ISIS, the creation and collapse of the caliphate, and the reconstitution of ISIS as ISKP. While Western influence and diplomatic blunders are well documented through this period, the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation are equally culpable. The editors would like to note that a vast majority of the 1.8 billion people who are adherents to some form of Islam are peaceful and reject all forms of religious violence.
Read Part Two: The complex history of Islamic extremism and Russia’s contribution to the rise of Al Qaeda and ISIS
Part Three – Efforts by the Soviets and the United States to contain Islamic extremism only helped it to spread
The rise of Saddam Hussein and the start of the Iran-Iraq War
After the death of his brother in an April 1966 plane crash, Abdul Salam Arif came to power in Iraq. U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson considered Arif a political moderate and saw an opportunity to improve U.S.-Iraq relations with the hope of tugging the Middle Eastern nation away from the Soviet Union. On June 5, 1967, while dialog between Baghdad and Washington was ongoing, the Arab-Israeli Six-Day War started. In response to the U.S. backing of Israel, Arif severed diplomatic relations.
Arif’s political opponents used the Six-Day War as leverage to push his new government to nationalize the foreign-owned Iraq Petroleum Company so he could use oil as an economic weapon. Behind the discord, the Arab Socialist Ba’ath Party was plotting a coup, with future president Saddam Hussein among the lead conspirators. On July 17, 1968, Arif’s government was overthrown in a mostly peaceful coup d’etat, installing Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr as president. After taking control, the new Ba’athist government announced it would embrace its current relationship with the Soviet Union and grow relations with the Chinese People’s Republic.
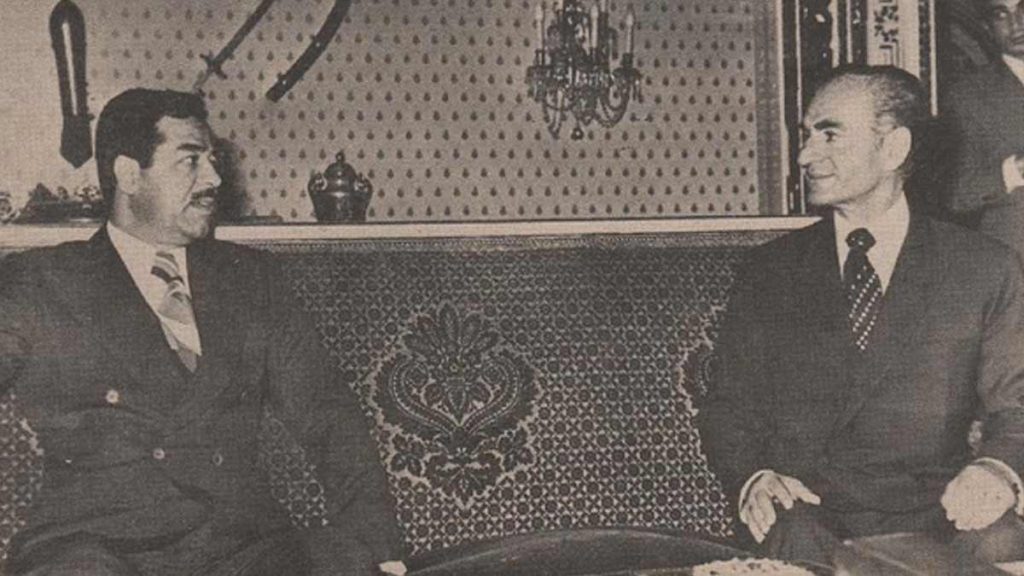
Vice President of Iraq Saddam Hussein (L) and Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, better known as the Shah of Iran (R), during the Algiers Agreement meetings in 1975
Credit – Photographer unknown – public domain
Hussein was named vice president of Iraq and led the full nationalization of the country’s oil industry, which was completed in 1972. At the time of the coup, relations between Iraq and Iran were poor due to Iran’s support of Iraqi Kurdish rebels. In late 1974, Hussein directed the Ba’athist government to improve relations with Iran, which led to the March 6, 1975, Algiers Agreement and two additional treaties also signed in 1975.
The Algiers Agreement aimed to settle maritime and territorial disputes in Iran’s Shatt al-Arab region and Iraq’s Khuzestan Province. Additionally, Iran agreed to end its support of the Kurdish Rebellion. After the agreement was signed, foreign relations significantly improved, ending almost a decade of isolation. The diplomatic success significantly expanded Hussein’s power.
After the signing of the Algiers Agreement, Hussein started an aggressive military modernization program, buying billions of dollars of hardware from the Soviet Union and France. In just 15 years, Iraq would build one of the largest conventional militaries in the world. In 1976, Hussein was named the General of the Iraqi Armed Forces while continuing to hold the office of vice president.
Around the same time, President al-Bakr’s health significantly deteriorated. Behind the veil, Hussein was already wielding presidential power and controlling the economy, the military, and foreign affairs. He used that control to become a feared strongman and started cultivating an inner circle of loyalists to take full control of the Ba’athist Party and the leadership of Iraq.
In 1979, President al-Bakr started negotiating with Syrian President Hafiz al-Assad for unification. If an agreement were reached, al-Assad would become the deputy leader of the combined nations, stripping Hussein of his power. On July 16, 1979, in what could be described as a one-man coup d’etat brought on by a health crisis, Hussein forced al-Bakr to resign and became the President of Iraq. Negotiations with Syria about unification immediately ended.
Despite the signing of the Algiers Agreement and the subsequent treaties, relations between Iraq and Iran were strained. The new leader of Iran, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, repeatedly called for the overthrow of the Iraqi Ba’athist government in jingoistic speeches due to Iraq’s embrace of secularism. The newly minted President Hussein praised the Iranian Revolution and Khomeini and called for renewed Iraqi and Iranian friendship and a mutual pledge to stop interfering with each other’s internal affairs.
The call for better relations was hollow and fell on deaf ears, and the diplomatic situation between Iran and Iraq quickly crumbled. On March 8, 1980, Iran recalled its ambassador and demanded that Iraq do the same. The next day, Iraq symbolically declared Iranian Ambassador Fereydoun Adamyat persona non grata.
Before the Islamic Revolution, Iran’s GDP was the largest among the 36 U.N.-recognized Greater Middle East nations. It had over 300,000 active-duty military personnel and was deep into a modernization program, buying billions of dollars of weapons from the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union.
One of the immediate outcomes of Khomeini’s rise to power was the embargo of parts, munitions, and other materials to maintain Iran’s military. Arrests and executions eliminated skilled and loyal military officers and pushed their subordinates into hiding. Iran’s military readiness was falling apart.
To deal with dissenters and political enemies, Khomeini created a personal guard, the paramilitary Islamic Revolution Guard Corps (IRGC), which would go on to be the terrorism-supporting arm of modern-day Iran. On April 30, 1980, Khomeini ordered the creation of the Organization for Mobilization of the Oppressed, better known as the Basij. The all-volunteer paramilitary was comprised of poorly trained and led men, most will little education. Often referred to as the 20 Million, during speeches, Khomeini would boast that with the Basij, no nation could defeat Iran.
During the first eight months of 1980, Iran and Iraq accused each other of over 1,200 border incidents, airspace violations, and maritime disputes. Hussein now viewed the Algiers Agreement as a mistake and recognized that he could use the post-revolution chaos in Iran to his advantage. He also saw an opportunity to engage the U.S. through the enemy of my enemy is my friend politics.
Hussein believed he had an opportunity to quickly take back the disputed Khuzestan Providence and its oil fields while expanding Iraq’s access to the Persian Gulf. On September 10, 1980, using the open issues of the Algiers Agreement as a casus belli, Iraq launched a limited military operation to seize the territories of Zain al-Qaws and Saif Saad. Twelve days later, the limited operation turned into a full-scale invasion of Iran, starting an eight-year war.
The Soviet Union becomes stuck in an Afghanistan quagmire
After the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan and completed its coup d’etat, Soviet troops launched a series of large-scale attacks in the central, northern, and western states of Afghanistan through 1985. While these large-scale attacks sometimes brought about temporary stability, the mujahadeen would retreat into Pakistan or deep into the mountains and return as soon as the Soviets withdrew.
Moscow had expected the Afghanistan army to do the majority of the fighting, with Soviet forces providing intelligence, logistics, close air support, and artillery. The opposite happened, with the local military units providing little support and frequently running from battles.
Soviet troops supported by the KGB and Afghanistan KHAD instituted brutal programs against the civilian population to try and find mujahadeen fighters, which only built more support for the Islamic rebel forces. However, the war was essentially a stalemate, and fighting against Soviet brutality made for odd bedfellows. With Western and Middle Eastern reporters embedded with mujahadeen, popular support in the Middle East, Europe, the U.S., and China rapidly grew. the mystique of chiseled-faced tribesmen bravely fighting against Russian tanks and helicopters on horseback was embraced as a noble struggle.
For Europe and the U.S., the fight within Afghanistan was seen as an extension of the Cold War. The Reagan Administration sought to destabilize the Soviet Union economically and diplomatically, with the Department of Defense budget swelling to $1.7 trillion in inflation-adjusted dollars.
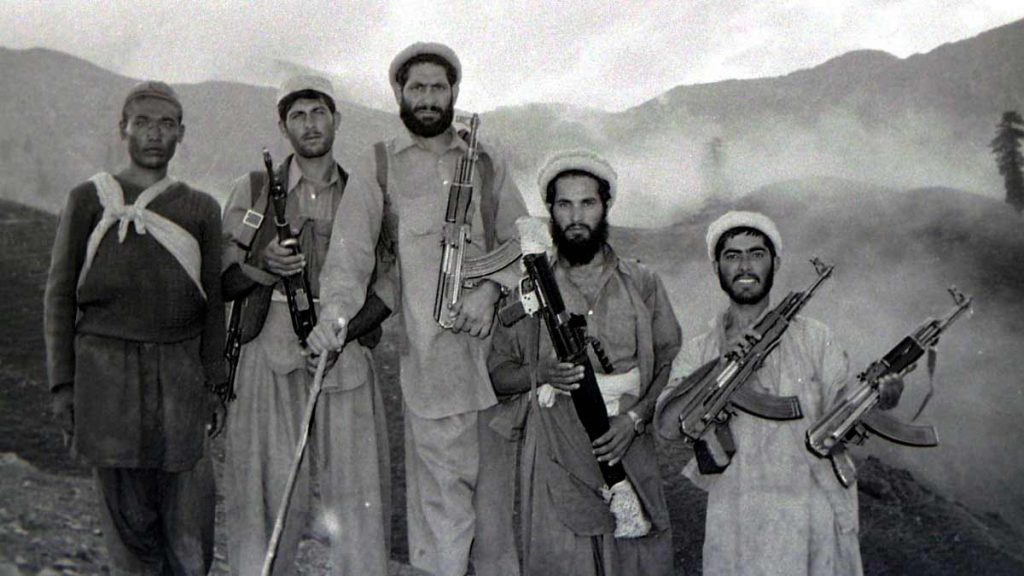

Mujahideen fighters in Afghanistan, 1985
Credit – Erwin Franzen, Creative Commons 2.0-4.0
The mujahadeen and other factions aligned against the Soviets were backed by the U.S., United Kingdom, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and China. Funding for Operation Cyclone, operated by the CIA, dramatically increased in 1986 and included the supply of Stinger antiaircraft missiles to the Afghan resistance. The Stinger provided SHORAD capabilities to the mujahadeen, tipping the balance of power on the battlefield. Russian aviation was practically grounded, and without air support, the number of Russian casualties increased significantly.
With the Soviet military stuck in an Afghanistan quagmire, another seemingly unrelated event would alter the course of world history. On April 26, 1986, after a failed safety test on Reactor 4 at the Chornobyl Nuclear Power Plant, technician Leonid Toptunov pushed the AZ-5 button meant to scram the reactor. Instead, due to a design flaw, Reactor 4 exploded, causing the worst nuclear accident in world history.
A combination of a failing and stagnant economy, the inability to keep up with Western defense spending, the war in Afghanistan, and the economic cost of cleaning up the Chornobyl disaster put the Soviet Union irreversibly on the path toward bankruptcy. The metaphorical rusting of the Iron Curtain and the Glasnost programs introduced by Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev permitted public criticism of the ongoing war in Afghanistan. Additionally, Gorbachev had been looking for an offramp since becoming Premier in 1985.
In 1987, with popular support for the war plummeting, Moscow announced it would start a controlled two-year withdrawal. For some, the announcement brought hope of a renewed Afghanistan. However, thousands of Islamic fighters didn’t come to fight for liberation. They choose to go to Afghanistan in response to the fatwas calling for the protection of historic Islamic lands from infidel invaders.
For some, like Osama bin Laden, the Soviet withdrawal announcement wasn’t the beginning of the end; it was the end of the beginning. What almost no one knew was bin Laden was already laying the foundation to form a new organization called Al Qaeda.
The United States embraces the Iran-Iraq War and pushes for a stalemate
In the first three months of the Iran-Iraq War, Iraq achieved multiple successes on the battlefield before momentum shifted. With relations already firmly established, Iraq was able to freely buy weapons and ammunition from the Soviet Union, France, and China. While the U.S. didn’t directly supply weapons to Baghdad, Washington lifted dual-use sanctions, which permitted the sale of civilian technology and heavy equipment that could be easily pressed into military service. And while declassified records show that no single nation provided Baghdad with the resources and technology to produce chemical weapons, companies from France, the U.S., West Germany, the U.K., and the Netherlands sold dual-use components, with France selling precursor chemicals to support the production of Sarin nerve gas.
Iran had deeper problems and could only find support from North Korea for weapons and ammunition and one other very unusual ally. Israel provided spare parts and ammunition for the existing Iranian arsenal of U.S. military technology. Tel Aviv believed that if Iraq won the war, its victory could empower Syria, which would present a broader threat to their sovereignty and stability.
While those were the publicly visible relationships, the U.S. was supporting both combatants. From 1981 to 1986, the CIA sold weapons to Iran through French shell companies. The profits were given to the Contras, who used the money to buy weapons to fight against the Soviet-backed Sandinista government in Nicaragua. When the Iran-Contra Affair was exposed, it blew up into a political scandal.
In 1986, Iranian forces captured the Fao Peninsula in Iraq, sending jolts through the West. Concern grew that Iran could win the war, spreading racial Islam across the Middle East. Due to support through the Iran-Contra Affair, Tehran started sharing military intelligence with Washington, which was already receiving military intelligence from Iraq. The 1986 Iran-initiated Tanker War didn’t help Tehran’s cause, and Kuwait and Saudi Arabia boosted military support to Iraq. To tip the balance of power back, Washington started sharing the Iranian military plans with Baghdad.
Iraq regained the initiative, pushed Iranian forces out of the Fao Peninsula, and on August 20, 1988, United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 ended the Iran-Iraq War. While both nations were left economically devastated, the Iranian military was an empty shell. One to two million people died, including at least 500,000 soldiers. The majority of the military dead were members of the Iranian Basij. Among the dead were at least 60,000 killed by chemical weapons, including 50,000 Iranians and 10,000 Iraqi Kurds.
For Hussein, the last eight years allowed him to transform into a brutal and feared dictator. With the war against Iran over, Hussein set his sights on a new military objective.
Tomorrow’s installment: The Soviets withdraw from Afghanistan, and Osama bin Laden becomes a cult of personality.
Read Part Three: The complex history of Islamic extremism and Russia’s contribution to the rise of Al Qaeda and ISIS